If you’ve been selling or processing payments in Europe or the United Kingdom over the past few years, then you’re probably familiar with the impact and requirements for Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) from the Payment Service Directive 2, or PSD2, which went into effect in late 2020 in the Europe Economic Area and in 2022 in the UK.
However, if your company is outside the EU and the UK and you have plans to sell into those territories, you may not be aware of your responsibilities for complying with PSD2 regulations.
That can be a costly mistake, as non-compliance can leave you vulnerable to an increase in declined payments, hurting your revenue. With a better understanding of PSD2 and how to stay compliant, you’ll be able to process global payments more efficiently and increase your sales.
What Is PSD2?
How Does PSD2 Impact Your Business?
PSD2 Compliance Requirements
Transactions Excluded or Exempt from SCA
How BlueSnap Can Help You Be PSD2 Compliant
The Takeaway: Ensure You Have 3-D Secure 2 or Risk Payment Declines
Your PSD2 Compliance Checklist
PSD2 FAQs
What Is PSD2?
PSD2 is a set of regulations pertaining to the European and UK markets. It was created to improve the existing rules for electronic payments and better integrate payment services across the European Union. The intent is to increase the protection level for consumers when they make electronic payments, and it impacts transactions that go through the European Economic Area (EEA) and UK in any capacity.
The regulations were part of series of updates designed to create a clear and comprehensive set of rules that apply to all existing and any new providers of innovative payment services. Post-Brexit, the United Kingdom continues to abide by PSD2 regulations within the UK market.
How Does PSD2 Impact Your Business?
Since any payment that goes through a bank in the EEA or UK must comply with PSD2 regulations, that can include when your shopper uses a credit or debit card issued by a bank in that region.
Merchants that are not based in the EEA or the UK can still be impacted by PSD2 compliance requirements. If your business sells online to buyers in these regions, your payment process should strive to be PSD2 compliant. Otherwise, it’s more likely that when you try to authorize transactions from those regions, they will be declined by the customer’s issuing bank.
 PSD2 Compliance Requirements
PSD2 Compliance Requirements
The PSD2 requirement that impacts businesses the most is Strong Customer Authentication (SCA).
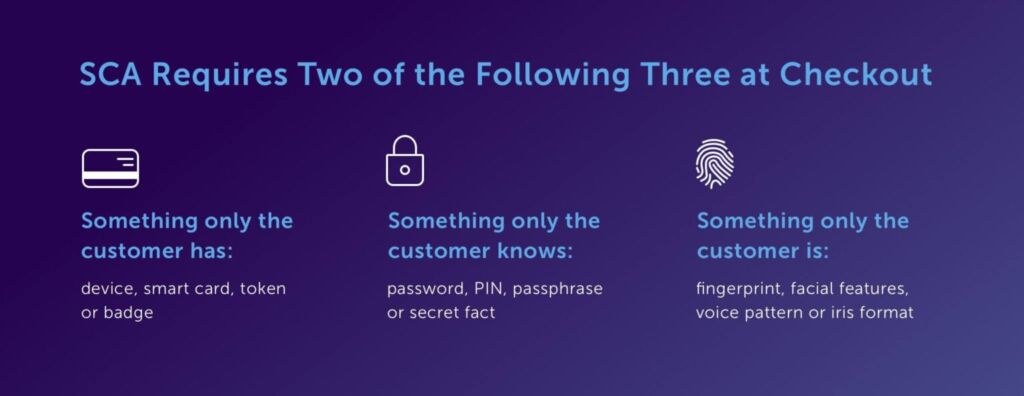
SCA requires businesses to implement two-factor authentication for online payments processed by a European acquiring bank. All merchants that process online payments in the EEA and UK must support an SCA solution. SCA requires at least two out of three unique customer identifiers:
- Something only the customer has: device, smart card, token or badge
- Something only the customer knows: password, PIN, passphrase or secret fact
- Something only the customer is: fingerprint, facial features, voice pattern or iris format
The goal of SCA is to reduce fraud by requiring merchants and issuers to validate consumers when they use electronic payment methods in the EEA and UK. So far, it has been highly effective. According to a European Banking Authority report, transactions with SCA see 70% to 80% less fraud than those without SCA.
While PSD2 restrictions do not apply to merchants outside the EU and UK, most (if not all) credit and debit card issuers within the EEA and UK will prefer to abide by it. If SCA is not used for a transaction, the payment is more likely to be declined.
While SCA is the most impactful piece of PSD2 compliance, it is not the only one. Other requirements include:
- Open APIs for Third-Party Access: One of the goals of PSD2 is to promote more payments competition within the EEA and UK. As a result, banks are required to provide open API access, which grants authorized third-party providers access to customer account information. Once a customer grants access, account information service providers should be able to access the relevant account data via API calls. Open APIs are also important for payment initiation, where the bank can push payments to authorized third parties.
- Greater Transparency: Under PSD2, companies need to provide as much transparency as possible when it comes to their terms and conditions, currency conversion rates and the full scope of what their financial products do.
- Faster Complaint Resolution: Payment service providers are also required to resolve complaints in a timely manner. As a result, incidents that fall under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) must be reported to EU regulatory bodies within strict time limits. For example, data breaches must be reported to a supervisory authority within 72 hours.
- No Credit Card Surcharges: PSD2 requires equality among payment methods, which means that sellers of any type aren’t allowed to add extra charges for processing card payments.
Transactions Excluded or Exempt from SCA
There are some EU and UK transactions that can be excluded from SCA requirements or considered exempt.
SCA Exclusions
Merchants may actively engage in certain transactions that are excluded from SCA requirements. These include:
- Low-Value Transactions: Transactions under 30 euros can be excluded from SCA because they are considered “low value.” However, the exclusion may not apply if the sum of previously exempted transactions since SCA was last applied exceeds 100 euros, or if there have been more than five consecutive excluded transactions.
- One Leg Out Transactions: One leg out transactions are payment transactions where one of the payment service providers, either the sender or the recipient, is based outside the EU or UK. It’s important to remember that, while SCA is not required for one leg out transactions, there could be consequences for non-compliance. For example, when a customer outside the EEA initiates a checkout transaction with an EEA merchant, that merchant’s payment service provider is still likely to request SCA authentication protocols from the customer’s bank. As a result, if the customer’s bank is not SCA-compliant, the transaction may fail.
- Merchant-Initiated Transactions: Any payment initiated by the merchant using previously stored card details, but without the consumer being actively involved, can also be excluded from SCA (provided the customer authenticates the first transaction using SCA). This differs from a recurring transaction, as those are required to happen at the same frequency/time and for the same amount. Merchant-initiated transactions don’t have those restrictions and allow for unscheduled payments or payments of differing amounts.
SCA Exemptions
Other transactions, which the merchant may have little to no control over how they’re initiated, can still be exempt from SCA requirements. These include:
- Transactions to Trusted Beneficiaries: A customer can create a list of trusted beneficiaries with their card issuer, in essence developing a whitelist. When the consumer initiates a transaction with any of these trusted beneficiaries, SCA is not required.
- Transactions Qualifying as Low Risk: Transaction risk analysis (TRA), as outlined in the Regulatory Technical Standards (RTS), allows payment providers to perform real-time risk analysis to determine whether to apply SCA to a transaction. Should the payment provider’s and cardholder’s banks both be below certain risk thresholds, then the transaction can be considered low risk and qualify for SCA exemption. However, when a payment cannot be qualified as low risk, then the payment service provider should default to SCA.
If you’re unsure which transactions qualify for SCA exemptions or exclusions, it’s better to be safe than sorry. Be sure to consult with a payments expert to ensure all your payments are meeting SCA requirements.
How BlueSnap Can Help You Be PSD2 Compliant
If you’re a merchant looking to start selling in the EU, whether your transactions are cross-border or you take advantage of local card acquiring, then you need to have SCA. 3-D Secure is the leading solution designed to satisfy the SCA mandate and helps make online transactions safer. The latest version of 3-D Secure (version 2.x) is more consumer-friendly than its previous version so transactions can remain frictionless and customers can buy with ease.
3-D Secure 2:
- Fills a number of functionality gaps, including mobile support
- Offers significant improvements to the user experience, including frictionless authentication
- Allows for a more seamless integration with businesses’ existing eCommerce solutions
Now, card issuers can send one-time security codes to cardholders via email, SMS or other more convenient channels. Biometrics like fingerprint scanning and facial recognition are now supported as well, allowing banks to validate transactions with minimum disruption to a customer’s workflow.
Luckily, even if you’ve never heard of 3-D Secure, you can easily use the solution from BlueSnap. Read our support documentation to learn how.
Stay Secure with 3-D Secure
Businesses that implement 3-D Secure 2 don’t only meet PSD2 compliance requirements but can also stop fraud, eliminate their liability for chargebacks related to authenticated transactions, and reduce their risk of cart abandonment. For more information, read 3-D Secure 2 FAQs.
Finally, understand that PSD2 regulations aren’t set in stone. The EU is still considering updates to transaction requirements and consumer protections, with work already begun on the framework for PSD3. Implementing a solution like 3-D Secure now can help future-proof you against upcoming changes.
The Takeaway: Ensure You Have 3-D Secure 2 or Risk Payment Declines
Now that you understand that neglecting to be compliant with PSD2 could impact approved transactions from customers in the EEA and UK, you can see how implementing 3-D Secure offers the solution.
If You Use BlueSnap for Payment Processing
No need to worry — BlueSnap is a licensed payment processor. Our platform supports 3-D Secure version 2.x, the latest authentication technology available for SCA compliance.
We’ve made it as quick and painless as possible for BlueSnap customers to set up 3-D Secure with BlueSnap, so contact us today to set it.
If You Use BlueSnap for Your Online Marketplace
Because we’re a licensed payment services institution that handles vendor payments, our marketplace payment solution has you covered. We provide compliant marketplace functionality in the same way we do for all online transactions.
BlueSnap customers should install the latest version of 3-D Secure to give their European customers the highest level of protection available. Contact us today to set up 3-D Secure 2 ASAP.
If You Are Not a BlueSnap Customer
BlueSnap offers several flexible solutions to help you build the secure payment experience that is right for your business. If you’re not a BlueSnap customer, get in touch today, so we can discuss the best, quickest path to PSD2 compliance for you.
Your PSD2 Compliance Checklist
Adhering to PSD2 regulations has some intricacies. We have developed a PSD2 Compliance checklist you can use as a reminder to make sure you’re meeting the requirements and to get the most out of selling into the EEA and UK:

Download a printer-friendly PDF of the checklist.
PSD2 FAQ
What is PSD2?
The Revised Directive on Payment Services (PSD2) is a set of regulations intended to establish a clear set of rules for payment providers across the EU and the UK. The intent is to better protect customers when they make electronic payments and to open up competition among providers.
What are the PSD2 requirements?
The major PSD2 requirement is the use of Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) for all online payments processed by an acquiring bank in the European Economic Area or United Kingdom. Other requirements include:
- The use of open APIs to allow authorized third parties to have access to accounts
- Greater transparency in a provider’s terms and conditions and the details of their financial products
- Resolution of complaints and reporting of security incidents within a set amount of time
- No credit card surcharges to ensure equity among payment methods
Who benefits from PSD2?
The intent of the PSD2 was to reduce the amount of fraud, increase competition and encourage the use of more local payment methods. As a result, customers can enjoy greater protection and security over their transactions and more options in how they conduct their transactions. It also opened the space for FinTechs to better compete with established banks.
Who must comply with PSD2?
If you are a merchant within the European Economic Area (EEA) or UK, then you must abide by all PSD2 regulations when processing transactions from an EEA or UK acquiring bank. If you are a merchant outside these territories, you are still impacted by PSD2 if the acquiring bank you use for payment processing is in either of those regions.
While some transactions may be exempt or excluded from needing to be PSD2 compliant, merchants can ensure their transactions are not declined by enacting Strong Customer Authentication.
What is Strong Customer Authentication?
Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) is a requirement in the European Economic Area and the UK that is intended to make online payments more secure. SCA requires at least two of the following unique customer identifiers for all transactions:
- Something only the customer has
- Something only the customer knows
- Something only the customer is
What is 3-D Secure?
The initial 3-D Secure was an advanced authentication solution that met the SCA mandate by verifying a cardholder’s identity in real-time. The current 3-D Secure 2.x is a more advanced payment authentication method that works across a range of devices, including mobile devices.
What is open banking?
Open banking is a system built on the use of application programming interfaces (APIs) to allow authorized third-party providers greater access to a customer’s financial data and banking account information.
When did PSD2 go into effect?
The following is the full timeline for the adoption of PSD2 regulations:
- 2007: The European Economic Area (EEA) enacts the very first Payment Services Directive (PSD) to create a unified payment market in the European Union.
- 2013: The EEA recognizes the need to update PSD based on technological changes and formulates the groundwork for PSD2.
- January 2016: EEA member countries vote to pass the PSD2 regulation to be enacted in 2018.
- June 2017: An open, harmonized API for the EEA is introduced, enabling third-party access under PSD2 standards.
- November 2018: Strong customer authentication measures are introduced under PSD2 to better protect consumers from digital payment fraud.
- January 2018: All EEA member states officially pass PSD2 and agree upon a future timeline for implementation.
- December 31, 2020: After multiple deadline postponements, PSD2 SCA officially goes live and in effect for all EEA member countries.
- September 14, 2021: PSD2 SCA goes live and in effect for the UK post-Brexit. The UK had voted in favor of PSD2 when it was still part of the EEA.
Related Resources:
- 5 Tips for EU & UK Businesses Selling Cross-Border
- The ISV’s Quick Guide to Navigating European Payment Regulations
- Thinking About Becoming a PayFac? Consider Payment Facilitator Compliance First
Frequently Asked Questions
What are payment regulations?
There are six key regulatory categories businesses must consider and adhere to when conducting any financial transaction:
- Payment network policies: These include any rules, regulations, guidelines or specifications put forth by payment networks, including EFT networks and Credit Card Associations.
- Data privacy: These regulations cover the rights given to individual data subjects concerning the personal data being stored (information like an individual’s name, email, location, online identifier, IP address, home address, etc.), including the right to prior notification of what the data is being used for, how it will be processed and when it will be deleted.
- Consumer security: These regulations protect consumers from fraud and theft, such as the Revised Directive on Payment Services (PSD2), enacted by the European Parliament, which requires Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) via three levels of identification for every transaction, from card number confirmations to texts with authorization codes.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards: Payment Card Industry (PCI) is a Data Security Standard (DSS), which is a set of requirements established by the major card companies to ensure that all businesses that process, store and/or transmit credit and debit card information maintain a secure environment. These standards help to defend against cyber-attacks, data hacks and other security breaches, which can result in extensive costs associated with loss of business, credit monitoring, post-breach audits and security updates.
- Tax collection: Tax responsibilities for businesses depend on a variety of factors such as the sales revenue, transaction volume and the location in which sales occur. In addition to the specific local tax laws, the payment model under which your business operates also has an impact.
- IT security: These regulations ensure that businesses are protected against hackers, cybersecurity regulations have been drafted to cover elements including data center redundancy, data storage, data recovery and other security investments.
What are cross-border payments?
Cross-border payments, or cross-border transactions, occur when the acquiring bank and the issuing bank are in different regions. When banks process cross-border payments, they perceive them to be riskier than domestic transactions, leading to higher fees and a greater likelihood of being declined.
What is local card acquiring?
Local card acquiring is when the acquiring bank and issuing bank are both in the same region. Using local card acquiring whenever possible reduces fees and increases authorization rates.
What is BlueSnap?
BlueSnap helps businesses accept global payments a better way. Our All-in-One Payment Orchestration Platform is designed to increase sales and reduce costs for all businesses accepting payments.
BlueSnap supports payments across all geographies through multiple sales channels such as online and mobile sales, marketplaces, subscriptions, invoice payments and manual orders through a virtual terminal.
And for businesses looking for embedded payments, we offer white-labeled payments for platforms with automated underwriting and onboarding that supports marketplaces and split payments.
With one integration and contract, businesses can sell in over 200 geographies with access to local acquiring in 45+ countries, 110+ currencies and 100+ global payment types, including popular eWallets, automated accounts receivable, world-class fraud protection and chargeback management, built-in solutions for regulation and tax compliance, and unified global reporting to help businesses grow.


 PSD2 Compliance Requirements
PSD2 Compliance Requirements