If you work for a software provider, either you’re considering some form of embedded payment service or your competition is. That’s because fintech has essentially become the fourth platform of the modern tech stack for all software businesses, along with internet access, cloud computing and mobile technology.
Credit Suisse predicts that the total market for embedded finance will be $800 billion by 2030 — and $500 billion of that will be payments. This growth in the embedded finance market for software platforms is not surprising as more and more businesses look for ways to offer financial services to their clients.
Here’s what you need to know about the basics of embedded finance, why it’s an increasingly important service for all industries and business models, and how you can seamlessly incorporate features like payments into your software for clients.
Embedded Finance Use Case Examples
How to Incorporate Embedded Finance into My Business
The Impact of Embedded Finance
What Is Embedded Finance?
Embedded finance is the integration of a financial product into a non-financial business or platform. This streamlines the financial process for end users, whether consumers or businesses, by allowing them to make all transactions directly at the point of service without needing to enter information on a third-party website.
So-called fintech “disruptor” banks were among the first to introduce banking-as-a-service, also known as BaaS, capabilities, such as mobile wallets or lending services. Today, you see numerous examples of embedded financial services, from purchasing travel insurance with your trip to wealth management services with stocks.
Thanks to modern APIs, software platforms can integrate a number of different types of financial services without relying on fintech. This allows independent software vendors (ISVs) to easily build financial integrations into their software platforms while a financial platform handles the complicated back-end financial processes.
Types of Embedded Finance
Hastened by the growth of eCommerce during the pandemic, embedded payments are the most common type of embedded financial service. The ability for ISVs to embed payment functionality as a service in their platforms allows their clients to accept payments without having to integrate another solution
As the technology around embedded finance has continued to develop, the types of available financial services have evolved to include:
- Embedded Credit: This includes Buy Now, Pay Later services and more. Embedded credit allows users to apply for and acquire credit within a platform. This is in addition to the ability to repay loans over time
- Embedded Insurance: Embedded financial technology allows software platforms to connect with insurance providers, which makes it easy to bundle insurance with products or services.
- Embedded Investments and Trading:This is the integration of stock market investment and trading, allowing users to make use of investment services such as account creation, funding and portfolio management.
Benefits of Embedded Finance
What makes embedded finance so powerful is that it provides end users immediate access to financial options while keeping them within a trusted, branded environment. For software platforms and their clients, offering a better experience ultimately leads to more revenue through increased customer retention and sales.
Let’s take a closer look at how embedded finance benefits software platforms, clients and user experience.
Software Platforms
- Embedding financial solutions to your platform can provide more value for clients, leading to better customer retention and lifetime value from your customer base. This itself can lead to a greater valuation of the software company, making it more attractive to potential investors and buyers.
- Embedded finance functionality can provide additional revenue streams and a boost in average order value as clients pay for the service and their customers spend more in transactions. This is another way in which embedded finance helps to increase the value of your software company.
- As more of your clients want this functionality, they’re going to come to you with their own preferred provider if you aren’t offering it in your software platform. Having to integrate third-party systems means investing additional time and resources to ensure everything works correctly. Alternatively, owning the financial process streamlines the integration with your clients.
- Embedded finance services are increasingly less about differentiation from your competitors and more about just keeping pace with expectations, as some clients might not entertain your business if you’re unable to provide those functionalities.
- Having a streamlined process for financial services can also open up new opportunities for cross-border transactions, making your platform a viable option for a larger global audience.
Clients:
- For software platforms’ clients, having embedded finance integrated into the software they already use means they do not need to look for additional vendors to support their business. Instead, they can enjoy the ease of working with a single platform — yours.
- Clients will appreciate being able to provide an improved experience for their own customers by being able to offer greater access to affordable financial services through a single platform.
- When provided with a suite of services, clients can select and customize the financial offerings to fit their customers’ needs.
Customers and End Users
- When customers are able to enjoy a comprehensive experience that includes embedded financial transactions, they encounter less friction in the process. This not only makes it more likely they’ll complete the transaction, but it increases their customer experience and loyalty.
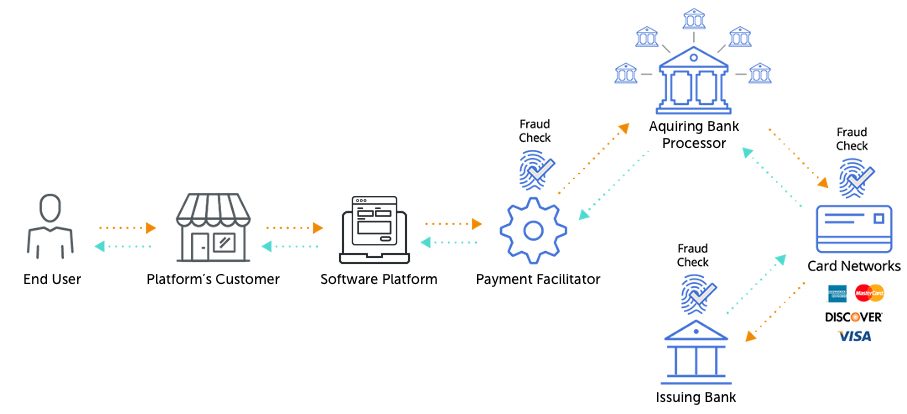
How Embedded Finance Works
While specific responsibilities and functions vary depending on the type of financial services provided, in general the key roles in the embedded finance ecosystem are:
- Software Platform: The non-financial ISV owns and operates a digital platform for clients, enabling them to offer a service or sell a product. This can be through a mobile or desktop application or a website.
- Financial Facilitator: This role connects the software platform and the institutions, enabling financial transactions. Financial facilitators use software development kits, often called SDKs, to import financial functionalities into the software platform and API tools to customize the available services
- Financial Institutions: The banks or other financial companies that manage and service loan requests, receive payments, offer credit and provide other financial services.
Here’s how the process works:
- The software platform embeds the financial facilitator’s technology into their platform, which is then leveraged by the platform’s clients to accept financial transactions.
- The software platform’s clients provide financial services, such as payments, credit applications or other transactions to their customers.
- When a transaction is initiated, the facilitator routes it to the appropriate banks, handling matters such as authorization, security and fraud detection.
- The end users, whether individual consumers or businesses, are able to conduct all of their business within a single experience.
For example, here is how an embedded payment process would look. It is similar to any other digital payment, but now the software platform that embedded the technology plays a role.
Embedded Finance Use Case Examples
Embedded finance can benefit any industry, but here are a few examples.
- Embedded Payments: Embedded payments have far-reaching benefits for many different fields. In education, for example, embedded payments allow parents to sign their children up for extracurricular activities and transportation, and then pay directly through the software portal instead of sending money with the student.
Similarly, in healthcare, patients are able to directly access their medical records, schedule procedures and make payments without having to wait for the mail.
In both instances, embedded payments help the businesses get paid faster without fewer concerns related to lost or late payments.
- Embedded Credit: Embedded credit options can pre-qualify end users for BNPL transactions. Payment solutions like Splitit allow customers to use a card they already have to make installment payments with no need to obtain additional cards or lines of credit. There is also no application or interest fees.
Embedded credit can also apply to B2B transactions, as invoice financing allows businesses to make larger purchases from their vendors and service providers and pay over time.
- Embedded Insurance: A game-changer for vehicle sellers, embedded or integrated insurance allows customers to directly purchase insurance through their own site, without having to find (or deal with the hassle of) a third-party insurance provider.
How to Incorporate Embedded Finance into My Business
Software platforms that want to embed financial functionality could build the infrastructure and support in-house, which can be a timely and costly process that requires considerable investment and deep expertise. Many software providers aren’t likely to have the internal resources or volume to warrant that investment.
The more efficient, cost-effective option is to partner with a provider. For example, when it comes to embedded payments, a third-party payment facilitator could offer the technology, expertise and maybe even more to help your business embed financial services. For example, BlueSnap Dash is our hosted option for vendors that want to offer embedded payments.
Alternatively, you can partner with a payfac-as-a-service provider where you get more control, such as with our BlueSnap RelayTM and BlueSnap FlexTM options:
- BlueSnap Relay is our quick-to-market, payfac-as-a-service, white-label offering, which shields you from risk while letting you brand your way.
- BlueSnap Flex is a branded embedded payment solution that leverages our API while you keep complete control.
No matter your choice, we can help you determine the best way to embed payments into your software platform.
The Impact of Embedded Finance
As embedded finance technology continues to develop, software platforms are increasingly likely to play a greater role in the distribution of financial services, like payments. We’re already seeing nontraditional financial providers becoming more popular options for financial services. Traditional banks are feeling the pressure to compete and are looking for their own ways to partner with digital platforms.
As businesses and consumers are provided more options for embedded financial transactions, they’re more likely to favor a brand or service based on a combination of superior convenience, personalization and cost.
As the most popular and widespread embedded finance solution, embedded payments are increasingly a “must have” function for all software platforms. Prospective clients will look for digital platforms that provide embedded payments in addition to their core services.
Interested in exploring your options for embedded payments? Talk to one of our payment experts to get started.
Related Resources:
- Embedded Payments: The Premium Way for Software Platforms to Offer Payments
- Increase Revenue as a Marketplace or with Embedded Payments? Find Out Which Is Best for Your Business
- What Software Providers Should Know About Embedded Payments for Their Platforms
Frequently Asked Questions
What are embedded payments?
Embedded payments are when payment functionality is embedded directly within a software platform, so clients do not need to integrate with another service to accept payments.
What are my options for embedding payments?
A few different models exist. You may be able to implement no- or low-code platform models without development help, but development resources are typically needed for implementations that have more customizable options. Depending on the model that you choose, your payments can be up and running in a day or two, or if you choose a more customizable model, a few months. You may also choose different fee structures, such as revenue sharing or buy rate.
How does embedding payments with a third-party partner work?
Using an embedded partner involves signing on with a partner that has developed embedded payments technology that your clients can access through your platform. The embedded payments partner will typically handle compliance, onboarding and customer support, depending on how you would like to structure the partnership.
What is BlueSnap?
BlueSnap helps businesses accept global payments a better way. Our All-in-One Payment Orchestration Platform is designed to increase sales and reduce costs for all businesses accepting payments.
BlueSnap supports payments across all geographies through multiple sales channels such as online and mobile sales, marketplaces, subscriptions, invoice payments and manual orders through a virtual terminal.
And for businesses looking for embedded payments, we offer white-labeled payments for platforms with automated underwriting and onboarding that supports marketplaces and split payments.
With one integration and contract, businesses can sell in over 200 geographies with access to local acquiring in 45+ countries, 110+ currencies and 100+ global payment types, including popular eWallets, automated accounts receivable, world-class fraud protection and chargeback management, built-in solutions for regulation and tax compliance, and unified global reporting to help businesses grow.